
By popular demand from our staff and community members, this edition of cybersec charcha will explore the basic digital security hygiene practices everyone should follow and how they protect your information from falling into the wrong hands.
As attacks like Pegasus gain more limelight and become part of public knowledge, many of us feel that there is nothing we can do to protect ourselves. And currently, this stands true for sophisticated attacks like Pegasus. However, it’s important to remain cognizant that every time someone’s data is compromised, it’s not because they were targeted with a military grade spyware. It’s crucial for us to be aware of our personal threat levels. This threat level can be determined through a process called Threat Modelling.
What is Threat Modelling?
Threat Modelling is a process of identifying your personal threat levels and creating your security plan accordingly. This is a good guide by EFF that outlines the questions you need to ask yourself when you are creating your personal Threat Model. A majority of the times when people’s PII (Personally Identifiable Information) is compromised, it’s because they failed to practice and implement basic digital security hygiene practices. The steps outlined below are the bare minimum measures you must have in place to protect your accounts online. Whereas nothing “guarantees” safety in a digital world, these measures sure do make your chances at remaining secure a lot better.
2 Factor Authentication
2 Factor Authentication (2FA) or 2 Step Verification or Multifactor Authentication is an extra layer of security used to make sure that people trying to gain access to an online account are who they say they are. Here’s how it works:
First, a user will enter their username and password. Then, instead of immediately gaining access, they will be required to provide another piece of information. There are multiple ways to provide this second form of authentication and some of them include SMS based authentication, Authenticator Apps, Push Notifications on the device linked to the account, Backup codes or using a physical authentication key like Yubikey. An important thing to remember is that SMS based authentication is not secure since text messages are not end to end encrypted and can be easily intercepted, which is why we don’t recommend this form of 2FA.
You can set up 2FA using Authenticator apps like Authy or FreeOTP or any other trusted service. This is one of the safest forms of 2FA as the OTP linked to your accounts in these apps change every 30 seconds. Moreover, no two OTPs are the same. So unless someone gains access to your password as well as the device you use for 2FA, it is very difficult for them to gain access to your account. Physical Authentication Keys are also one of the most secure forms of authentication, however, setting them up could be difficult for people who aren’t very tech savvy. Push Notifications are also considered to be fairly secure and have been made the default method of authentication for many services these days.
Regardless of which method of 2FA you opt for (except SMS based!), it is necessary to make sure that it is turned on for every service you use in the digital space to make your accounts more secure.
Setting Strong Passwords
We sound like a broken record every time we put the words “strong passwords” in this newsletter, but that’s only because this is really important! Even though passwords are not the strongest or safest mode of authentication (which is why enabling 2FA is key!), they are still the first line of protection for your accounts. It’s critical that the passwords you use match the following criteria:
- Each account should have a completely unique password than the rest of your accounts. And no, password123 and password456 are not different passwords!
- They shouldn’t include any PII (Personally Identifiable Information) like your DOB, partners / parent’s names or any other information that is easily available in the public domain.
- They should be long (many resources suggest more than 15 characters) and a mix of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Use a password manager to manage and generate complex passwords. More on this in the section on password managers.
Passphrases >>> Passwords
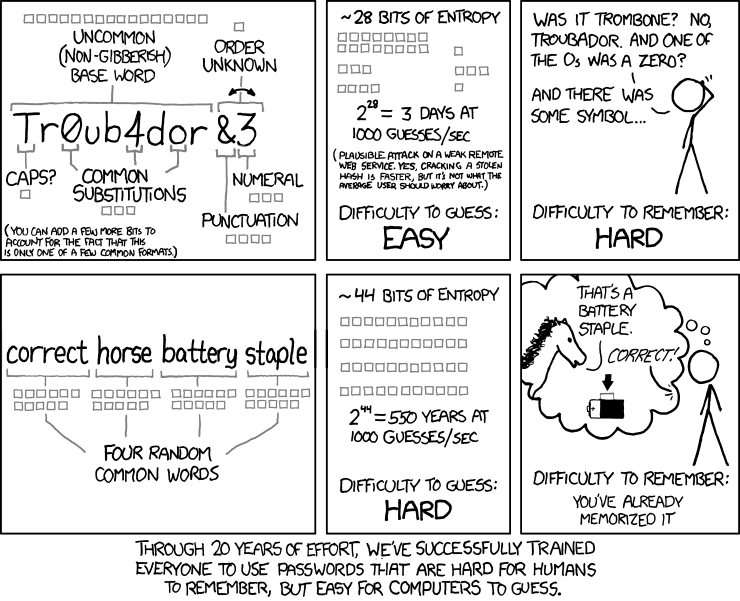
This is a really important one. Passphrases are secret keys consisting of a sequence of words or other text as a form of authentication. The reason why passphrases are more widely recommended than passwords are because they are long, easy to remember and hard to guess. An added advantage that most Indians have is also the ability to speak 2 or more languages. You can even set a passphrase in your native language, which will be very difficult for people who don’t speak your mother tongue to crack! Here's a cool tool by EFF that let's you generate random passphrases easily.
Using Password Managers
This is probably one of the most important steps you can take to secure yourself. Remember when we said you shouldn’t repeat the same password/phrase for different accounts? The issue that most of us face there is how do you remember complex passwords that are different for each account. At this point, most of us have passwords for so many different services, it’s hard to keep track. This is where a Password Manager steps in to save the day!
What is a Password Manager?
A password manager can be an online or an offline computer program that allows users to store, generate, and manage their passwords for local applications and online services. It assists in generating and retrieving complex passwords and storing such passwords in an encrypted database. Access to your password manager will be only dependent on you remembering your Master Password that will give you access to your other passwords. If you start using a password manager, you only have to memorize your master password and the credentials for the rest of your accounts can be stored and accessed easily without you having to remember each of them.
Most password managers also come with other features like Autofill and Generate Random Passwords. In some instances, the autofill feature can also help identify phishing websites, especially if this is a website for which you have stored a password in your manager already. The Generate Random Passwords feature helps you generate complex passwords without having to actually come up with one. The best passwords are the ones you don’t remember! Bitwarden and LastPass are good examples of online password managers, whereas a service like Keepass is a trustworthy offline password manager service.
Identifying Phishing Attacks
Phishing is a form of social engineering that involves counterfeit communications that seem to come from a credible source but which can compromise all types of data sources. Sometimes the goal of a phishing attack can be gaining access to your personal data and financial information for monetary gain. In other cases, phishing emails are sent to gather employee login information or other details for use in more malicious attacks against a few individuals or a specific company. Phishing as a type of cyber attack is growing everyday. People need to learn about them to protect themselves and ensure email security throughout an organization.
How does it work?
Phishing starts with a fraudulent email or other communication designed to lure a victim. The message is made to look as though it comes from a trusted sender. If it fools the victim, they are coaxed into providing confidential information, often on a scam website. Sometimes malware is also downloaded onto the target's computer.
Best hygiene practices to avoid falling for a phishing scam:
- Be wary of emails from strangers and verify information like check name and email address before engaging with them.
- Phishing emails lure victims by using emotions like fear, urgency, curiosity or greed. Be suspicious of emails marked “urgent” or ones that use similar vocabulary to get you to click on links.
- Notice mistakes in spelling and grammar.
- Beware of generic greetings, “dear sir/ma’am”.
- Don’t be lured by incredible “deals”.
- Hover over the link before you click / copy paste the link in a fresh browser tab to ensure it has a secure URL (i.e. https://).
- Never give out personal or financial information based on an email request.
- Don’t trust links, images or attachments in unsolicited emails or text messages from unknown senders and don’t click on them.
- The Autofill feature of password managers can also be helpful in identifying phishing attempts.
Other important practices to be implemented to secure yourself:
- Keep your device softwares updated with the latest versions. Software updates often come with the latest security patches for vulnerabilities and it’s crucial to update your apps and device softwares regularly.
- Encrypt your devices and maintain encrypted backups.
- If your threat model requires this, practicing device compartmentalization is also a good idea. This is an easy read on what device compartmentalization is and how to implement it.
In other news…
1. Apple patches a zero-day vulnerability exploited by NSO
Yesterday, Apple released a security patch for a zero-day vulnerability that affected all iPhones, iPad, Macs and Apple Watch. Citizen Lab who initially discovered the vulnerability said that this zero-day flaw (named as such because it gives developers 0 days to roll out a fix) exploited a flaw in Apple’s iMessage, which was then exploited to push the Pegasus Spyware. Apple has urged all their users to update their devices ASAP to implement the fix. If you are a user of any of these Apple products, update your devices immediately!
2. Why you need to secure your printer and how to do it
We recently stumbled upon a useful article on the need to secure your printers. Whereas we generally spend a lot of time securing our laptops and phones, printers often remain neglected. They remain a common gateway for hackers to break into your company or home networks. If cybercriminals get their hands on your printer, they can access sensitive or confidential information stored on your printer, send unauthorized print jobs among other things. This step by step guide by Cybernews is super helpful if you want to secure your printers.
3. Protonmail shared an activists’ IP address to cooperate with Swiss Law enforcement
Protonmail is an End-to-end encrypted email service that is widely used by people who are looking for options for secure email communications. Early this month, Protonmail drew criticism as it shared an activists’ IP address with law enforcement authorities leading to their arrests in France. Despite its earlier claims that the company stores no IP logs, which have since been modified, they acknowledged that while it's illegal for them to abide by requests from non-Swiss law enforcement authorities, it will be required to do so if Swiss agencies agree to assist foreign services such as Europol in their investigations. It’s also important to remember that E2E encryption protects your data, not your metadata. There are a few steps that can be taken to protect your metadata like IP Address by using Tor Browser, however, general advice by security experts suggests that it’s best not to use emails for sensitive communications.
That's all for this edition of our newsletter! If you like reading Cybersec Charcha, don't miss the next edition by signing up for the newsletter so it can be directly delivered to your inbox every month. Lastly, if you like the work IFF does, become a member or make a one time donation to help sustain our work in the long run!
